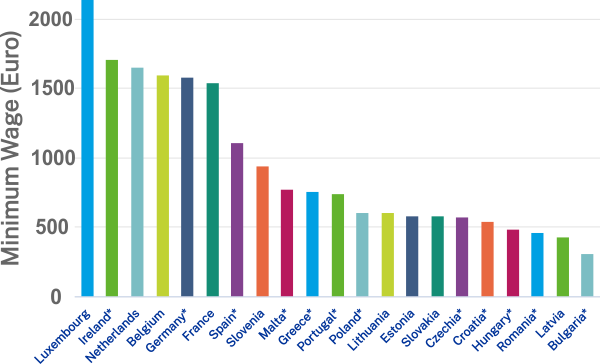
The term ‘minimum wages’ usually refers to the lowest rate payable by employers to workers in a particular country or industry (for example, Cyprus has different statutory rates for different occupations). The European Union (EU) in November 2017 set out a commitment to fair wages across EU and aimed at all workers in the EU should earn a fair and adequate wage, no matter where they live by 2024.
Below is an overview of the ‘minimum wages’ across 21 EU countries as of Jan 2020.
‘Clicking’ on each country name or the column would open an additional chart showing the evolution on minimum wages since Jan 2010 for that country.
data source: Eurofound
* For comparison across the 21 EU countries for which data is available,
- the wages in Bulgaria, Croatia, Czechia, Hungary, Poland and Romania were converted to Euro according to the exchange rate applicable at the end of previous reference month;
- in case of Greece, Portugal and Spain which has more than 12 payments per year, the annual sum of the minimum wage was divided by 12 calendar months;
- in Germany and Ireland where the minimum wage is defined as an hourly rate, the monthly wages were calculated by multiplying by the number of usual weekly hours;
- in Malta, where the minimum wage is defined at weekly frequency, the monthly wages were calculated by considering 4.33 weeks per calendar month.